-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 24
Understanding Swagger
- What is Swagger?
- How does Apigee 127 use Swagger?
- Help me with YAML
- Understanding the Swagger specification file
Swagger™ is a specification and framework implementation for describing, producing, consuming, and visualizing RESTful web services.
To read more about Swagger, refer to:
The Swagger Editor for Apigee 127 lets you design your API specification and preview its documentation for your Apigee 127 API. This editor is part of Apigee 127, and it is installed with Apigee 127.
Use this editor to configure the swagger.yaml configuration file. A basic version of the file is provisioned with every new Apigee 127 project, and lives in <project_root>/api/swagger/swagger.yaml. It conforms to the Swagger 2.0 specification.
Behind the scenes, Apigee 127 Swagger middleware validates and processes the Swagger configuration file, and routes API operation endpoints to controller files. All you need to do is implement your custom API controller logic.
Try it:
a127 project create test-projectcd test-projecta127 project edit
YAML is a data serialization/representation standard. If you're new to YAML, check out www.yaml.org. Another excellent introduction is the Uncyclopedia YAML entry.
YAML is intended to be easy for humans to read. Every Apigee 127 project includes a Swagger 2.0 compliant configuration file that is written in YAML.
When you execute a127 project create myproject, a default Swagger model is placed in myproject/api/swagger/swagger.yaml. This model conforms to the Swagger 2.0 specification.
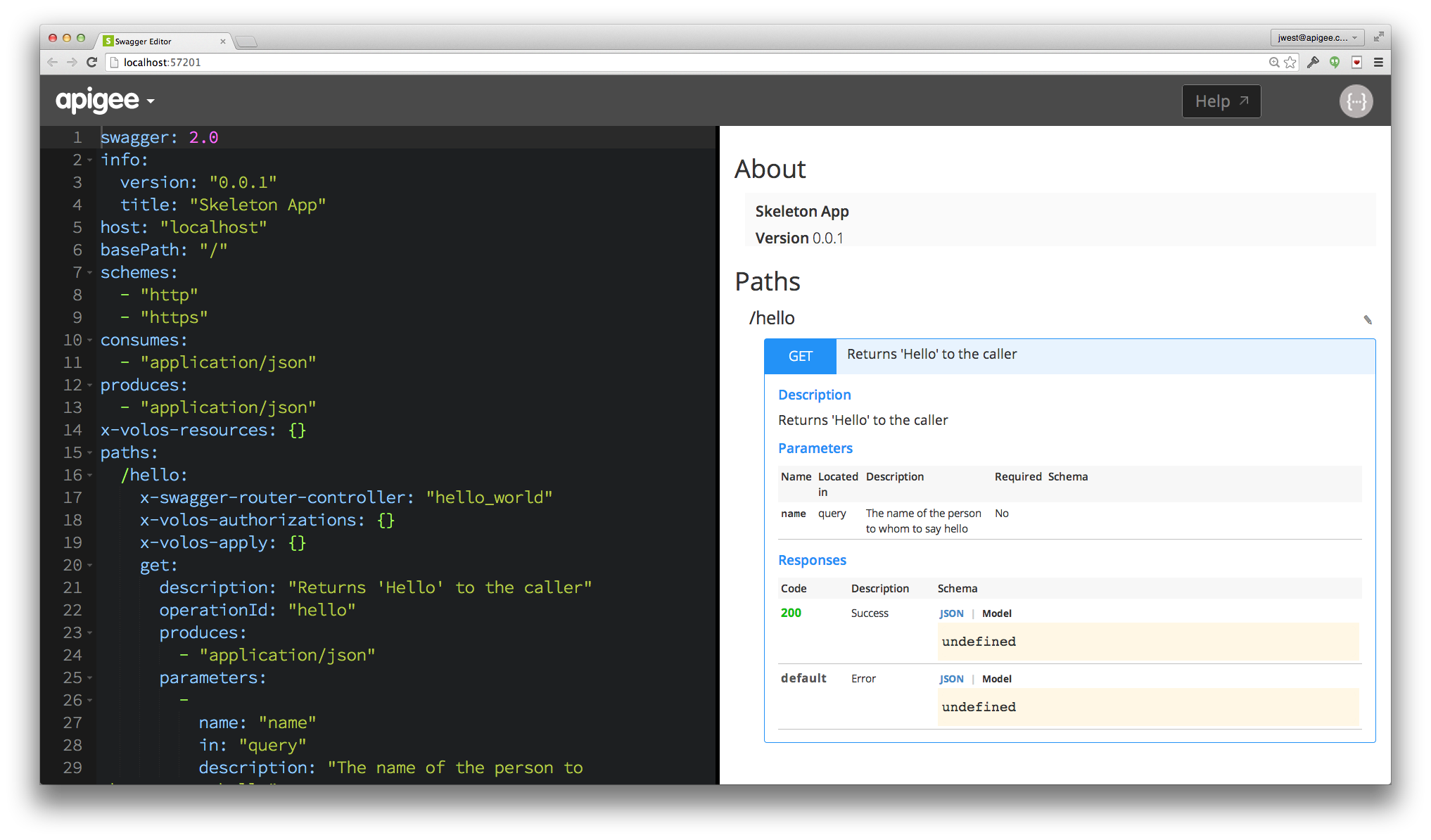
Here is the entire swagger.yaml file that is provisioned for a new Apigee 127 project:
swagger: 2.0
info:
version: "0.0.1"
title: "Skeleton App"
host: "localhost"
basePath: "/"
schemes:
- "http"
- "https"
consumes:
- "application/json"
produces:
- "application/json"
x-volos-resources: {}
paths:
/hello:
x-swagger-router-controller: "hello_world"
x-volos-authorizations: {}
x-volos-apply: {}
get:
description: "Returns 'Hello' to the caller"
operationId: "hello"
produces:
- "application/json"
parameters:
-
name: "name"
in: "query"
description: "The name of the person to whom to say hello"
required: false
type: "string"
responses:
200:
description: "Success"
schema:
$ref: "#/definitions/HelloWorldResponse"
default:
description: "Error"
schema:
$ref: "#/definitions/ErrorResponse"
definitions:
HelloWorldResponse:
required:
- "message"
properties:
message:
type: "string"
ErrorResponse:
required:
- "message"
properties:
message:
type: "string"The Swagger file includes a number of standard Swagger 2.0 specification elements. You can read about them in the Swagger 2.0 specification.
Here's a brief description of the elements in the Apigee 127 Swagger file:
-
swagger: 2 - (Required) Identifies the version of the Swagger specification (2.0).
-
info: - (Required) Provides metadata about the API.
-
host: - (Optional) The host serving the API. By default, a new project connects to a server running locally on port 10010.
-
basePath: - (Optional) The base path on which the API is served, which is relative to the host.
-
schemes: - (Optional) A list of transfer protocol(s) of the API.
-
consumes: - (Optional) A list of MIME types the APIs can consume.
-
produces: - (Optional) A list of MIME types the APIs can produce.
-
x-volos-resources: - (Optional) A custom Swagger extension for the volos-swagger module. The volos-swagger module lets you add Volos.js features like quotas, caching, and OAuth 2.0 to your API by configuring them in the Swagger file. For more information, see the volos-swagger README file.
-
paths: - (Required) Defines the available operations on the API. You'll spend most of your time configuring the paths part of the file. You can read about the path element in the Swagger 2.0 specification. In general, the paths section specifies an operation's verb (like
get), the endpoint for an API operation (like/hello), query parameters, and responses. -
definitions: - (Optional) These represent the structure of complex objects such as request and response bodies. For example, you might have a collection of
/usersthat returns an array ofuserobjects. You would describe these with two definitions: 1) to describe theUserobject, and 2) the definition of theUsersarray. Swagger uses JSON-schema.
In the Apigee 127 Swagger file, the paths section also includes these custom extensions:
-
x-swagger-router-controller: - (Optional) This extension specifies the name of the controller file (hello_world.js) that will execute when this API operation is called. Controller files reside in
apis/controllersin your Apigee 127 project. This extension is provided through theswagger-toolsmiddleware module, which is included when you require thea127-magicmodule in your main Node.js app. -
x-volos-authorizations: - (Optional) This extension applies Volos.js authorization to the API operation. You can use this extension to add OAuth 2.0 security, for example. For more information, see the volos-swagger README file.
-
x-volos-apply: - (Optional) This extension applies specified volos modules, and they use the configurations specified in the x-volos-resources extension, described previously. For more information, see the volos-swagger README file.
Having Trouble? Try posting your question to the Apigee Community. Or, for more links and resources, check out our Help Page
| Need help? Visit the Apigee Community ! |
|---|
-
Getting started
-
Add policies to your API
-
Add security policies
-
Deploy your projects
-
Programmatic hooks
-
Good to know about
-
Deep dives
-
Reference topics
-
Troubleshooting and getting help
-
Related resources