-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 24
What is Apigee 127
Apigee 127 provides the tools you need to design and build Enterprise-class APIs entirely in Node.js and deploy them on any Node.js runtime system.
Apigee 127 includes:
-
A [Swagger 2.0 Editor] swagger-editor running locally, built for the Swagger Community by Apigee
-
[Swagger Tools] swagger-tools-github middleware for Node.js including Message Validation, Authorization and Routing
-
[Volos.js] volos-github middleware for value-added functions such as Caching, Quota and OAuth 2.0
-
A Node.js version of [apigeetool] apigeetool-github for deploying your application to Apigee Edge
-
[Apigee 127 Command-Line Interface] a127-cli for managing project lifecycle
-
An easy-to-manage local Usergrid usergrid runtime and portal
The focus of Apigee 127 is using a standard model for building APIs. From this standard model, Apigee 127 middleware can infer a lot from your API, such as:
- What type of resources are needed to make it run
- What authorization scopes should be applied to which paths?
Combining the Node.js swagger-tools and Volos.js middleware modules, Apigee 127 enables you to quickly build robust, high quality APIs by offloading a lot of the work needed to do so. From the Swagger 2.0 model, Apigee 127 creates the server-side flows and middleware specified in the Swagger specification, leaving the core logic of the API up to API developers.
The programming flow for an Apigee 127 project looks like this:
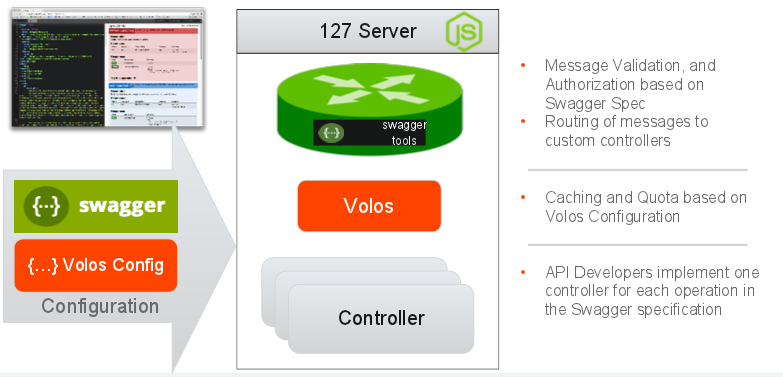
-
Define the Swagger Model using the Swagger 2.0 Editor included with Apigee-127.
-
Annotate your resources and operations in the Swagger 2.0 model with the
x-swagger-router-controllerextension to define the name of the Controller that implements the logic behind the operation. For example:
paths:
/hello:
x-swagger-router-controller: "hello_world" - Utilize the
operationIdproperty for your operations in the Swagger 2.0 Model
get:
description: "Returns 'Hello' to the caller"
operationId: "hello"- Optionally use the Volos.js Swagger Extensions to define Caching, Quota and OAuth configuration:
x-volos-resources:
cache:
provider: volos-cache-memory
options:
name: name
ttl: 10000
quota:
provider: volos-quota-memory
options:
timeUnit: minute
interval: 1
allow: 2
oauth2:
provider: volos-oauth-apigee
options:
key: *apigeeProxyKey
uri: *apigeeProxyUri
validGrantTypes:
- client_credentials
- authorization_code
- implicit_grant
- password
passwordCheck: passwordCheck- Optionally apply Volos.js functions to individual operations to add caching, quota and OAuth security to your API. You can integrate
volosfeatures directly into your Swagger model using the Volos.js Swagger Extensions or implement them programmatically in the Node.js app. Example:
/twitter:
x-swagger-router-controller: twitter
x-volos-authorizations:
oauth2: {}
x-volos-apply:
cache: {}
quota: {}
get:
...-
Behind the scenes, Apigee 127 wires up your app, routing HTTP requests to specific Node.js controller files.
-
At runtime the
swagger-routerwill validate & authorize the request before sending it to thehellooperation of thehello_worldcontroller which is found in{project_home}/api/controllers/hello_world.js. By default the swagger-router looks for controllers in[project_home]/api/controllersbut this can be overridden in the project. -
If configured, Volos.js Middleware will handle Caching, Quota and/or OAuth authorization
-
Finally, your controller logic will be invoked according to the
x-swagger-router-controllerspecified for the resource path and theoperationIdof the corresponding operation. By default the Controller should be in[project_home]/api/controllers/[x-swagger-router-controller].js -
You can develop and test your API locally using the command
a127 project start -
Once you are ready to deploy your API it can run anywhere Node.js can run anywhere:
- Apigee Edge
- custom servers in your datacenter
- Other PaaS providers that support Node.js such as Heroku or Amazon Elastic Beanstalk.
** However, to take advantage of the full suite of Apigee's value-added services the API should be deployed there.
Having Trouble? Try posting your question to the Apigee Community. Or, for more links and resources, check out our Help Page
| Need help? Visit the Apigee Community ! |
|---|
-
Getting started
-
Add policies to your API
-
Add security policies
-
Deploy your projects
-
Programmatic hooks
-
Good to know about
-
Deep dives
-
Reference topics
-
Troubleshooting and getting help
-
Related resources